Cells divide to make more cells. This is called cell division. It helps living things grow and repair. Mitosis is a type of cell division. It is very important for growth and development. Without mitosis, our bodies wouldn’t grow or heal properly.
This article will explain what mitosis is. We will look at the stages of mitosis and why it is important. We will also use pictures to help you understand better. Finally, we will answer common questions about mitosis.
By the end, you will know how mitosis works and why it is crucial for life.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division that makes two identical cells from one cell.
The purpose of mitosis is to help organisms grow and repair damaged tissues. During mitosis, the cell’s DNA is copied. Then, the cell splits into two equal daughter cells. Both new cells have the same DNA as the original cell. This process ensures that each new cell functions properly. Mitosis is different from meiosis. Meiosis makes cells for reproduction.
Mitosis is essential for life. It keeps our bodies growing and healing.
Stages of Mitosis:
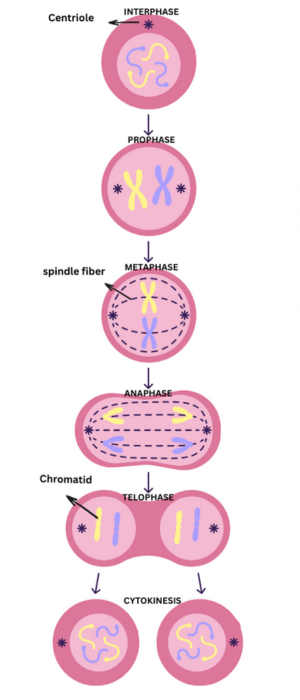
Prophase
In prophase, the DNA in the cell coils and forms visible structures called chromosomes.
Each chromosome has two identical parts called sister chromatids.
The nuclear membrane, that surrounds the nucleus, starts to break down and disappear.
Spindle fibers, which are long protein strands, begin to form from structures called centrioles.
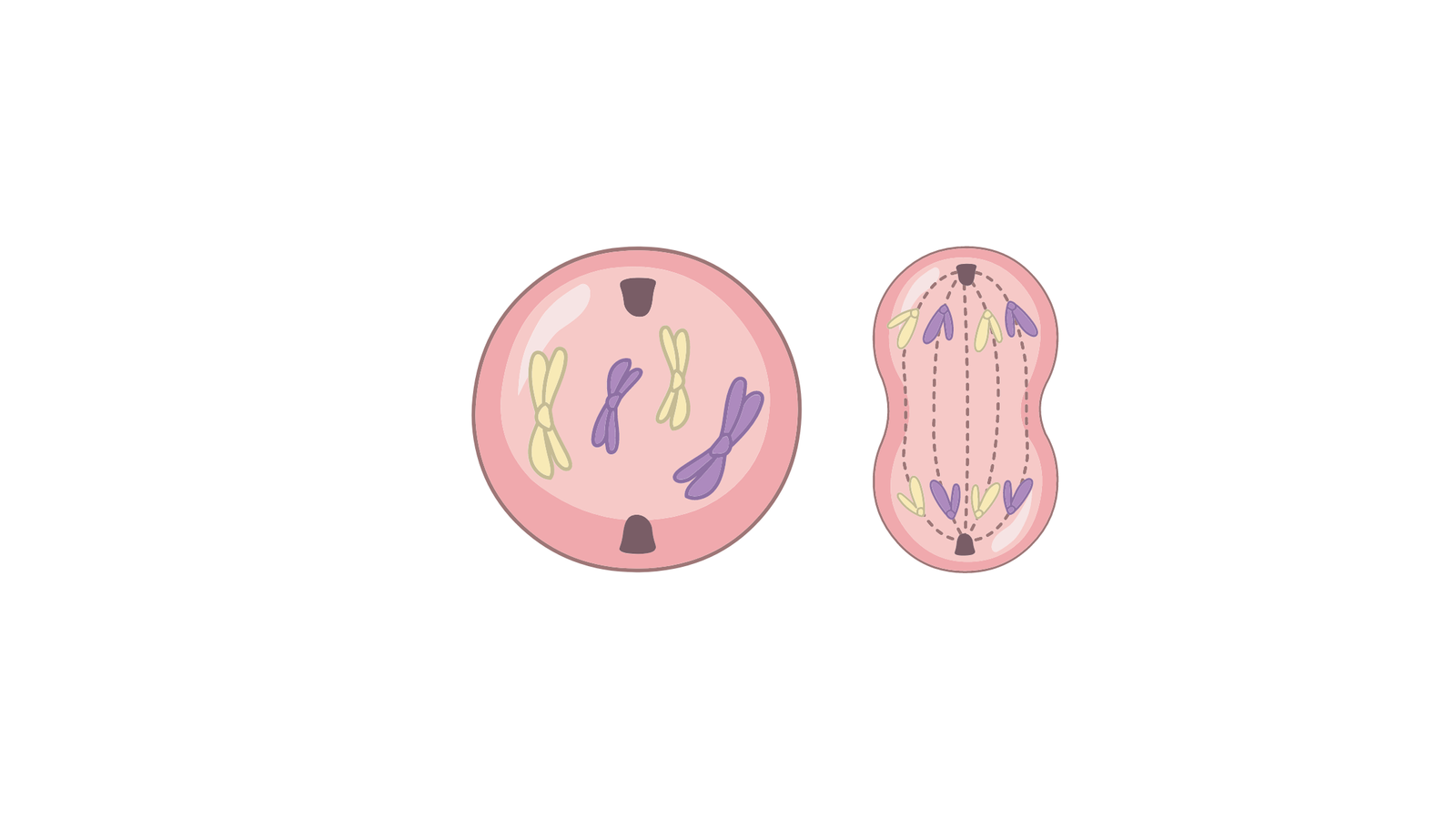
Metaphase
The chromosomes in the metaphase line up in the middle of the cell. This area is called the equator or metaphase plate.
Spindle fibers attach to the center part of each chromosome, called the centromere.
This ensures that each new cell will get a copy of each chromosome.
Anaphase
During Anaphase, the spindle fibers separate the sister chromatids by pulling them apart.
Each half of the chromosome, now called a daughter chromosome, moves to opposite sides of the cell.
This step ensures that each new cell has the same number of chromosomes.
Telophase
In telophase, the daughter chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell.
A new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two nuclei.
The chromosome becomes less visible as it begins to uncoil into chromatin.
Cytokinesis
This is the final step of the process of Mitosis.
The cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two separate, identical daughter cells.
Each new cell has the same number of chromosomes and the same DNA as the original cell.
Cytokinesis ensures that the process of mitosis is complete and that both new cells can function properly.
Role in Growth and Repair
Mitosis makes new cells.
These new cells replace old or damaged cells.
This process helps us grow and heal.
For example, when you cut your skin, mitosis makes new skin cells.
Importance in Maintaining Genetic Stability
Mitosis ensures new cells have the same DNA.
This keeps genetic information stable.
Each new cell works just like the original cell.
Examples of Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cells
Mitosis helps plants grow taller and make new leaves.
In animals, mitosis helps grow new skin, bones, and muscles.
Both plants and animals rely on mitosis to repair damaged tissues.
Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
|
Feature |
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
|
Purpose |
For growth and repair |
For making reproductive cells |
|
Number of Cells |
Produces 2 identical cells |
Produces 4 unique cells |
|
Chromosome Number |
Cells have the same number of chromosomes |
Cells have half the number of chromosomes |
|
DNA Replication |
Happens once before the division |
Happens once before the division |
|
Stages |
4 stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase |
8 stages: 2 rounds of division |
|
Cell Type |
Occurs in body cells |
Occurs in reproductive cells |
|
Genetic Variation |
Produces identical cells |
Produces different cells |
|
Examples |
Skin cells, muscle cells |
Eggs and sperm |
Mitosis helps organisms grow and repair by creating two identical cells.
Meiosis creates reproductive cells with half the DNA, leading to genetic diversity.
Conclusion
Mitosis is important for life. It is important for the growth and development of our body.
It helps us grow, heal, and keep our DNA the same in new cells.
Understanding mitosis helps us know more about how our bodies work.
Call to Action
Explore more articles about cell biology.
Subscribe for updates to keep learning about science and biology.