Enzymes are protein molecules that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies. Enzymes play a vital role in assisting digestion and functions of the liver. Having the right amount of each enzyme is crucial for good health. Too much or too little of a certain enzyme can lead to health problems.
For example, too little of the enzyme lactase can cause lactose intolerance, leading to digestive issues with dairy products. Conversely, an excess of some enzymes can lead to digestive disorders or other health issues.
What are Digestive Enzymes?
Digestive enzymes are special proteins that help break down large food molecules into smaller parts, called building blocks. They are part of a group known as hydrolases.
Hydrolases split food molecules by adding water. This process helps turn big molecules into tiny ones that can be used by the body.
Digestive enzymes work outside cells, mixing with food as it moves through the gut. This is different from most enzymes, which work inside cells.
The process of digestion depends on these enzymes. They are made by cells in the gut and organs like the pancreas. These small parts then pass through the gut wall into the bloodstream. From there, they travel to the liver and other parts of the body where they are used.
How Do Digestive Enzymes Work?
Enzymes are proteins with specific shapes. They are made of long chains of amino acids. They have a special area called the active site. This active site binds to molecules called substrates.
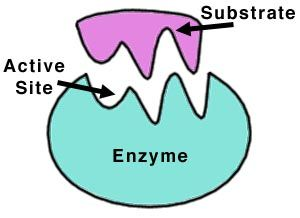
Here’s how the process works:
- Recognition and Binding: The enzyme’s active site fits the substrate like a key fits a lock. This specific fit allows the enzyme to recognize and bind to the substrate.
- Formation of the Enzyme-Substrate Complex: Once the enzyme and substrate bind, they form a temporary structure called the enzyme-substrate complex.
- Chemical Reaction: Within this complex, the enzyme lowers the energy needed for a chemical reaction. This makes it easier for the substrate to be broken down or transformed.
- Product Formation: The enzyme helps break the substrate into simpler molecules. These simpler molecules are called products.
- Release of Products: After the reaction, the products are released from the enzyme’s active site. The enzyme is now free to bind with another substrate and repeat the process.
Types of Digestive Enzymes
Digestive juices and enzymes |
Substance digested |
Product formed |
| Saliva Amylase |
Carbohydrate (Starch) | Maltose |
| Gastric juice Protease (pepsin) and hydrochloric acid |
Proteins | Partly digested proteins |
| Pancreatic juice Proteases (trypsin) Lipases Amylase |
Proteins Fats emulsified by bile Carbohydrate (Starch) |
Peptides and amino acids Fatty acids and glycerol Maltose |
| Intestinal enzymes Peptidases Sucrase Lactase Maltase |
Peptides Sucrose (sugar) Lactose (milk sugar) Maltose |
Amino acids Glucose and fructose Glucose and galactose Glucose |
| Bile from the liver Bile salts |
Fats globules | Fat droplets |
Benefits of Digestive Enzymes in Digestion
Digestive enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down food into nutrients that our body can use. Here’s why they are important:
Digestive enzymes help us break down the food in our body. Here’s why they are so important:
- Speed Up Digestion: Enzymes speed up the breakdown of food. Without them, the digestion process would be too slow. This means our bodies would not get the nutrients they need in time.
- Break Down Large Molecules: Food is made of large molecules like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Enzymes break these large molecules into smaller pieces. For example, enzymes break down starch into sugars, proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Improve Nutrient Absorption: Once the food is broken down into small molecules, it can be easily absorbed by the intestines. This helps the body take in important nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and energy.
- Prevent Digestive Issues: Proper enzyme function helps avoid digestive problems. For example, the enzyme lactase breaks down lactose in dairy. Without enough lactase, people can get bloating and gas from dairy products.
- Support Overall Health: Enzymes are crucial for good health. They ensure that our bodies get the nutrients needed to stay strong and healthy. Proper digestion helps us stay energized and active.
- Maintain Balanced Digestion: Enzymes help keep digestion balanced. They ensure that food is broken down properly and waste is removed effectively.
Role of Digestive Enzymes in Gut Health
Digestive enzymes are crucial for maintaining good gut health. Here’s how they contribute:
- Break Down Food Efficiently: Enzymes help break down large food molecules into smaller ones. This process makes it easier for the gut to absorb nutrients. Efficient digestion prevents food from sitting too long in the gut, which can lead to discomfort.
- Prevent Digestive Disorders: Proper enzyme function helps prevent common digestive issues like bloating, gas, and indigestion. For example, the enzyme lactase breaks down lactose in dairy products, preventing symptoms of lactose intolerance.
- Maintain Healthy Gut Flora: Digestive enzymes aid in breaking down food particles that can affect the balance of gut bacteria. Properly digested food helps maintain a healthy balance of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Support Nutrient Absorption: Enzymes help convert food into nutrients that the gut can absorb. This ensures the body gets essential vitamins and minerals. Good nutrient absorption supports overall health and energy levels.
- Reduce Inflammation: Efficient digestion reduces the risk of inflammation in the gut. When food is properly broken down, it helps prevent irritation and inflammation, which can contribute to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Promote Regular Bowel Movements: By breaking down food effectively, enzymes help ensure that waste moves smoothly through the digestive tract.
- Aid in Digestive Comfort: Proper enzyme activity helps the gut process food comfortably. It reduces the chances of discomfort caused by undigested food particles fermenting in the gut.
Natural Sources of Digestive Enzymes
Enzyme |
Source |
Benefits |
| Amylase | Mango, bananas, and sweet potatoes | Helps break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. |
| Protease | Pineapple (bromelain), papaya (papain), Kiwi (actinidain), Ginger (zingibain) | Breaks down proteins into amino acids. Bromelain; helps digest proteins and has additional anti-inflammatory effects ginger may also help ease nausea. Papain; helps digest proteins and is a popular meat tenderizer. Kiwi is high in fiber to support digestive tract function |
| Lipase | Avocados, dairy products, Sauerkraut, kimchi | Facilitates the breakdown of fats into fatty acids and glycerol, enhancing metabolism. Fermented foods generate enzymes during fermentation, along with probiotics (which is a beneficial bacteria) that support digestive health. |
| Lactase | Yogurt, kefir | Helps digest dairy products. The lactase enzyme in Kefir assists in breaking down the fermented milk, making it potentially tolerable for some individuals with lactose intolerance. |
| Sucrase | Fruits like mangoes and peaches | Breaks down sucrose (table sugar) into glucose and fructose. |
| Maltase | Whole grains and malted foods | Converts maltose into glucose. |
| Nuclease | Leafy greens, asparagus | Breaks down nucleic acids into nucleotides. |
Digestive Enzyme Deficiency:
If you have a digestive enzyme deficiency, you might notice the following symptoms:
- Gas and Bloating: You may feel gassy and bloated after eating due to undigested food in your gut.
- Abdominal Cramping: You might experience stomach cramps or discomfort because food is not being broken down properly.
- Diarrhea or Oily Stools: You could have diarrhea or see oily stools, as undigested fats can cause these symptoms.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: You might lose weight without trying, as your body is not absorbing nutrients effectively.
The symptoms above can also be the signs of other health conditions. If you have digestive symptoms that last more than a week or two, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation. They can help determine if you have a digestive enzyme deficiency or another condition.
Digestive Enzyme Supplements
Digestive enzyme supplements can help people with enzyme deficiencies or digestive issues. Digestive enzyme supplements are pills or powders that contain enzymes to help break down food in the digestive system. They can help reduce symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea. It’s important to choose the right type of enzyme supplement based on your needs.
Conclusion
Enzymes play a crucial role in our bodies, supporting many vital functions. Digestive enzymes, in particular, are essential for breaking down the food we eat into smaller, absorbable nutrients. They help transform large molecules like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates into simpler forms, which our bodies can easily use for energy and growth.
Without enough digestive enzymes, our bodies struggle to process food efficiently. This can lead to symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea, and can affect overall health and nutrient absorption. Enzyme deficiencies may require specific treatments or supplements to aid digestion and relieve symptoms.
Overall, enzymes are fundamental to maintaining good health. They ensure that our digestive system works properly, help prevent digestive disorders, and support effective nutrient absorption. By understanding and managing enzyme functions, we can improve our digestive health and overall well-being.