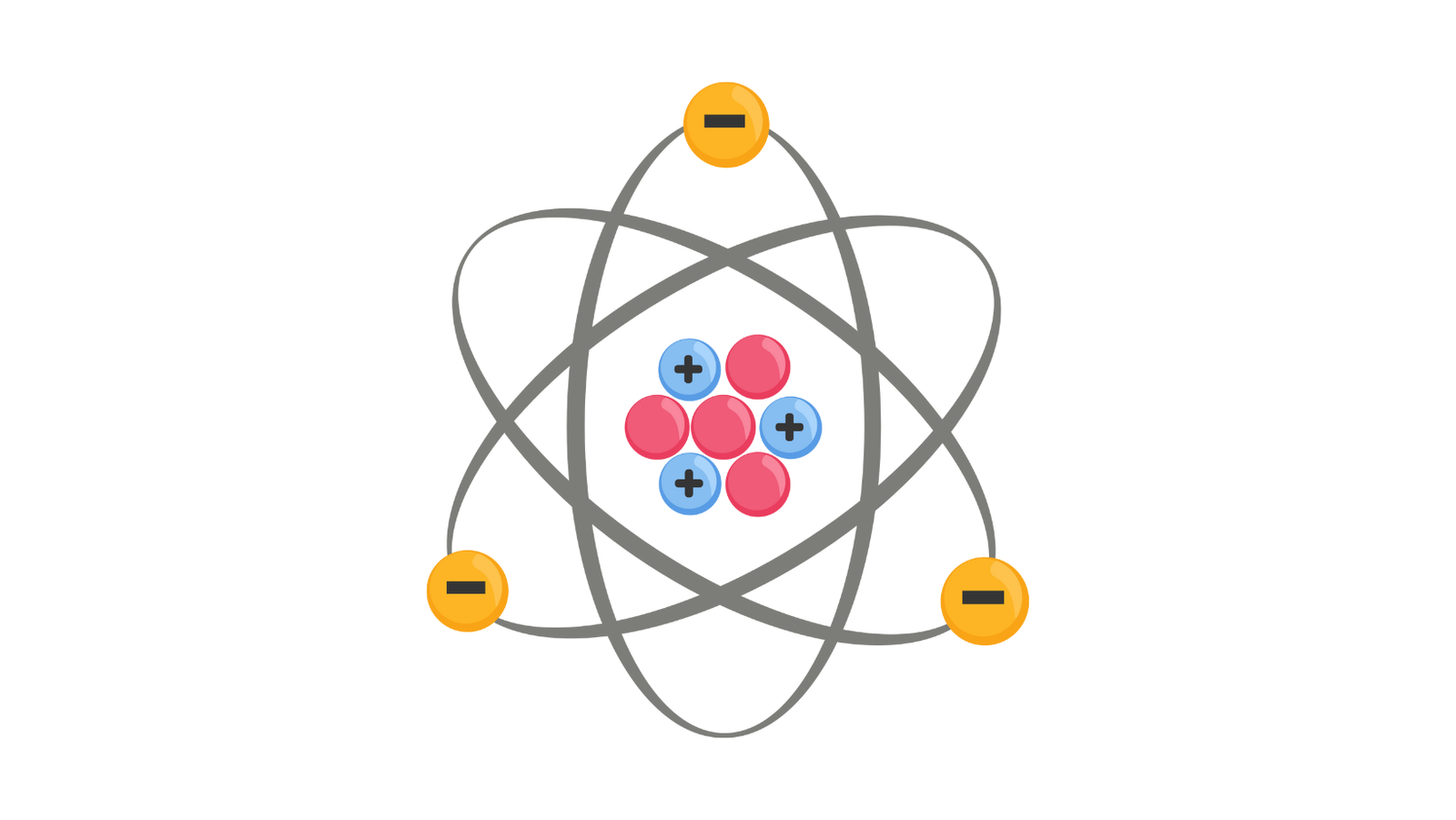
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of particles within an atom. Atoms have a nucleus containing protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit this nucleus at various energy levels. Protons have a positive charge, while electrons have a negative charge.
The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom defines the element. Neutrons add mass but have no charge. Whereas, electrons determine the atom’s reactivity and bonding. The atomic structure forms the basis for understanding chemical reactions and properties.
Atomic Models
Atomic models help us understand the structure of atoms. These models have evolved over time with new discoveries. Early scientists proposed various theories based on experiments. Each theory and model has its strengths and restrictions.
The development of atomic models began with simple ideas. These ideas became more complex as technology improved. Scientists used experiments to refine their theories. Atomic models are fundamental to chemistry and physics.
-
Thomson Atomic Model (limitations as well for all):
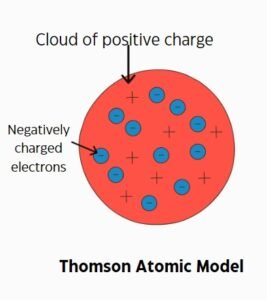
J.J. Thomson proposed the Thomson atomic model in 1897. He discovered electrons and suggested atoms are like “plum pudding.” In this model, electrons are scattered within a positively charged sphere. This model was the first to include subatomic particles.
The Thomson atomic model was a significant step in understanding atomic structure. It introduced the idea of negatively charged electrons. Thomson showed that atoms are not indivisible. This was a major advancement in atomic theory.
However, the Thomson atomic model had limitations. It couldn‘t explain the atom’s stability. It also failed to describe the existence of a nucleus. These issues required further investigation and new models.
Despite its flaws, the Thomson atomic model was crucial. It paved the way for future discoveries in atomic theory. Scientists built on Thomson’s work to develop more accurate models. His contributions remain important in the history of science.
-
Rutherford Atomic Theory:
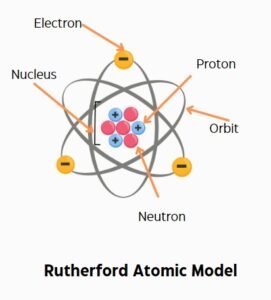
Ernest Rutherford proposed the Rutherford atomic theory in 1911. He conducted the famous gold foil experiment. This experiment proves that atoms have a small, dense nucleus. The nucleus contains protons and most of the atom’s mass.
Rutherford’s atomic theory was a breakthrough. It disproved the Thomson atomic model. Rutherford showed that electrons orbit the nucleus. This model introduced the concept of a central nucleus in atomic structure.
However, the Rutherford atomic theory had limitations. It couldn’t explain how electrons remain in stable orbits. It also didn’t address the energy levels of electrons. These issues needed further research and refinement.
Despite its flaws, the Rutherford atomic theory was important. It laid the foundation for the modern atomic model. Scientists like Niels Bohr built on Rutherford’s work. Rutherford’s contributions remain key in understanding atomic structure.
-
Daltons Atomic Theory:
John Dalton introduced his atomic theory known as Dalton atomic theory in the early 19th century. He suggested that all matter consists of indivisible atoms. Dalton’s theory states that atoms of a given element are identical. He also said atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
Dalton’s atomic theory was a major advancement in chemistry, providing a systematic explanation for chemical reactions. Dalton’s ideas helped scientists understand the nature of matter. His theory formed the basis for modern chemical science.
However, Dalton’s atomic theory also had its own limitations. Dalton’s theory also couldn’t explain isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different masses. These discoveries came after Dalton’s time.
Despite its flaws, Dalton’s atomic theory was crucial. It established the concept of atoms in science. Dalton’s work paved the way for future discoveries in atomic structure. His contributions remain fundamental to chemistry and atomic theory.